How to Use a Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fractures?
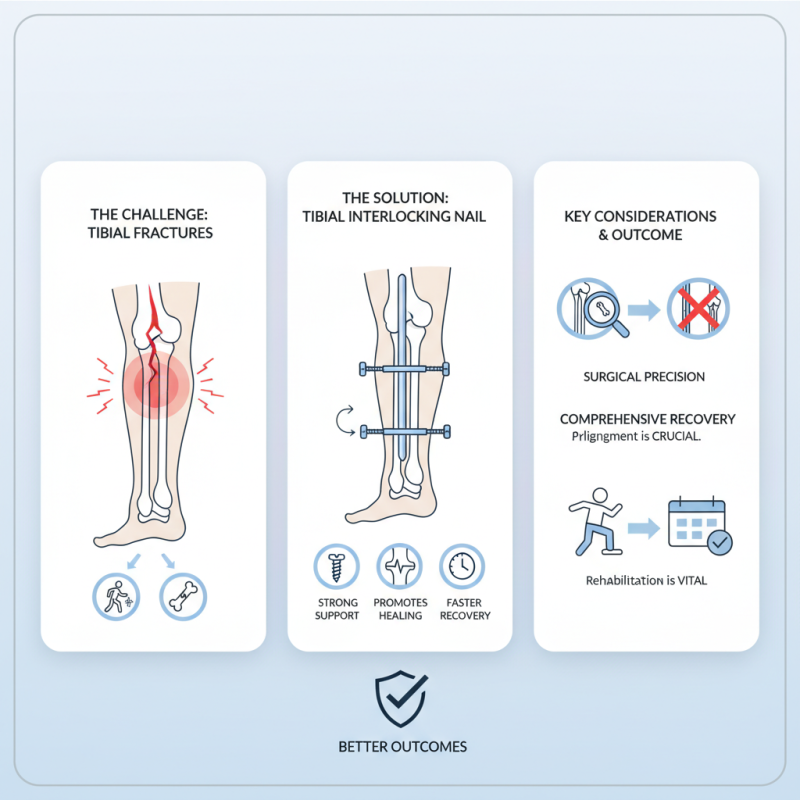
Fractures of the tibia can significantly impact a person's mobility. Effective treatment is crucial for a full recovery. One innovative solution for severe bone fractures is the Tibial Interlocking Nail. This device is designed to stabilize the fractured bone and promote healing.
The Tibial Interlocking Nail offers several advantages. It provides strong internal support, allowing for early weight-bearing. Surgeons insert the nail through a minimal incision, which can lead to quicker recovery times. However, the process is not without challenges. Proper alignment during insertion is vital. Any misalignment could lead to complications. Patients often need rehabilitation after the procedure, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Despite its benefits, the use of a Tibial Interlocking Nail requires careful consideration. It's essential to assess the type and severity of the fracture. Each case is unique, and what works for one patient may not be suitable for another. Reflecting on these details can help ensure better outcomes for those dealing with tibia fractures.
Understanding Tibial Interlocking Nails: Overview and Indications
Tibial interlocking nails have become a standard treatment for certain bone fractures. These devices are particularly effective for long bone fractures, especially in the tibia. According to recent studies, they provide stability and promote healing. Data from the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma indicates a success rate of approximately 90% in union for fractures treated with interlocking nails.
Understanding when to use tibial interlocking nails is essential. They are recommended for complex fractures, such as those that are comminuted or have significant displacement. The ability to secure the fracture while allowing for some motion across the site promotes quicker recovery. However, inadequate surgical technique can lead to complications. Reports suggest that improper placement can result in malunion or nonunion, necessitating further interventions.
Moreover, tibial interlocking nails are not suitable for every patient. Certain conditions like severe soft tissue injuries may contraindicate their use. There is a risk of infection at the surgical site, which occurs in about 5-15% of cases. Surgeons must weigh these risks against the benefits. It is crucial to have open discussions with patients regarding their specific situation and expectations.
How to Use a Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fractures? - Understanding Tibial Interlocking Nails: Overview and Indications
| Indication | Patient Profile | Procedure Overview | Post-Operative Care |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tibial shaft fractures | Adults with stable fractures | Insertion of nail through medullary canal, securing with interlocking screws | Pain management, monitoring for infection, mobilization exercises |
| Bilateral tibial fractures | Patients with multiple injuries | Similar to single fracture, can be done in stages | Enhanced rehabilitation, tailored physiotherapy regimen |
| Fractures with bone loss | Patients requiring additional support or fixation | Use of bone graft in combination with interlocking nail | Regular check-ups to assess bone integration and healing |
| Complex fractures | Patients with comminuted or fracture-dislocation injuries | Careful planning, often requires orthopedic consultation | Long-term follow-up, assessment of alignment and function |
Preoperative Assessment: Evaluating Patient and Fracture Type
Preoperative assessment is critical in using a tibial interlocking nail. Proper evaluation of both the patient and the fracture type can significantly influence surgical outcomes. Research shows that fractures involving the tibia account for about 35% of all long bone fractures. Understanding the fracture pattern, displacement, and patient health is essential.
A thorough understanding of the fracture site leads to better planning. For example, a classified fracture, such as an open fracture versus a closed fracture, requires different management strategies. Open fractures are prone to infection, which complicates healing. This assessment helps in deciding the perioperative antibiotic therapy. In a study published by the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, early identification of fracture types led to improved healing rates by 20%.
Tips: Always review the patient's medical history. Chronic conditions, like diabetes, can affect healing. Evaluate nutritional status as well. Malnutrition can delay recovery. Engage in discussions with the surgical team about the potential risks. A multi-disciplinary approach may lead to better patient outcomes. Engage with a nutritionist, for instance, to optimize the patient’s condition pre-surgery.
Surgical Technique: Steps for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
The tibial interlocking nail is a common method for treating bone fractures. Proper technique is essential for success. The first step involves preparing the surgical site. Make sure to clean and drape the area well. This will help reduce infection risk.
Next, achieve proper access to the fracture site. Incisions are made carefully. Accurate placement is crucial. Use fluoroscopy to confirm alignment. This step helps avoid errors. Misalignment can lead to complications.
After the nail is inserted, secure it with locking screws. Check stability before closing the incision. It's vital that the nail holds the fracture firmly. However, there’s a risk of over-tightening the screws, which can damage bone tissue. Reflection on each step improves future performance. Surgeons must always focus on precision and adjust based on patient needs.
Postoperative Care: Managing Recovery and Complications
Postoperative care after using a tibial interlocking nail includes monitoring for complications. Patients may experience pain and swelling at the surgical site. It’s essential to manage these symptoms promptly. Regular pain assessments help determine if medications are effective. If pain persists, it may require different treatments. Swelling can interfere with healing, so elevating the leg is often recommended.
Another key aspect is physical therapy. Start with gentle range-of-motion exercises. This encourages blood flow and prevents stiffness. Gradually increase activity as advised by the healthcare provider. However, it's crucial to listen to your body. Patients should avoid pushing through pain. Complications like infections can arise, so watch for signs such as increased redness or discharge. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor recovery progress and adjust care if necessary.
Postoperative Recovery Duration for Tibial Interlocking Nail Surgery
This bar chart illustrates the average recovery time in weeks for patients of different age groups who underwent tibial interlocking nail surgery. Younger patients tend to have a shorter recovery duration compared to older individuals, reflecting variations in healing rates.
Rehabilitation Protocol: Restoring Function After Tibial Nail Surgery
Rehabilitation after tibial nail surgery is essential for restoring function and mobility. The process often takes time, and patience is crucial. Initially, rest is vital to allow the body to heal. Elevate the leg to reduce swelling. Use ice packs for comfort, but remember to take breaks. Gentle movements can help maintain circulation.
As you progress, engaging in light physical therapy is necessary. Start with simple exercises like ankle pumps. Focus on gradually increasing your range of motion. Balance exercises can aid stability and prevent falls. It’s essential to listen to your body. If discomfort arises, adjust your activities accordingly.
Tips: Set small, achievable goals. Celebrate each milestone, no matter how minor. Consider keeping a journal to track your progress. Remember, the journey may have ups and downs. Some days will feel better than others, and that’s okay. Stay motivated, and don’t hesitate to ask for help.

